ESTATE PLANNING MANAGEMENT

What is WILL?
In term of language means ordering, advising, promising or giving after death in a document.
- WILL is a person’s lifetime commitment to his or her estate to be executed after his or her death for the purpose of a charity authorized under SYARIAH LAW.
Why should we need WILL?
- Easily get him a warrant or an administrator. Therefore, all Muslims who have assets are proposed to make a will, and it can be mentioned in the will that he gives all the inheritance to his heirs according to ISLAMIC LAW.
If we die without a letter of inheritance, then the heirs will have a lot of problems managing the estate.
Also, avoiding family conflicts rather than having the will of ther process distrubiting property is a bit tricky.
Is it true that no assets means we’re not required to prepare a WILL?
- The WILL is not just an order for the distribution of property. However, it is also an order to appoint WASI to his estate. If the owner of the property is in debt, he is obligated to settle it and he is obliged to make a will.
- In addition, the owner of the assets may also make an order to appoint any guardian to his minor, or specify that the assets held is not his and to be returned to the original owner. That is, any order that does not conflict with ISLAMIC LAW can be stated In the will document. If not,it will goes back to FARAID DISTRIBUTION.
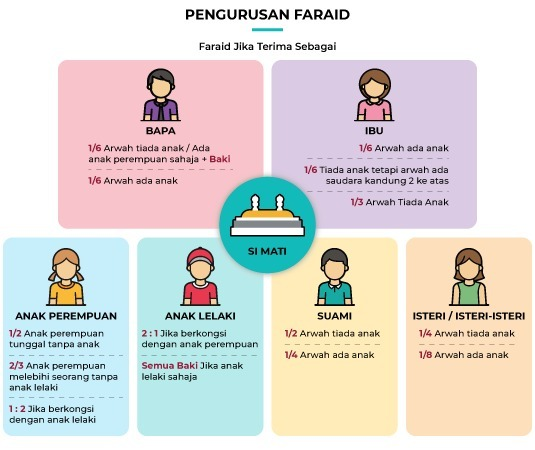
What is FARAID?
in terms of language it means PERMANENCE
According to the Terms, Faraid is the distribution of the estate after the death of an Islamic person who has been established under Islamic Law on such legally entitled heirs (Children, Wife, Husband, Mother, Father, etc.)
The property distributed to the heirs is the remainder of the property left after deducting all the management of the corpse, the debts of the heirs of any form of religion (Zakat, Nazar etc.) or all the debts of the people and the fulfillment of the will of the Islamic State.
Law on Faraid: –
- Distribution of inheritance according to Islam following the death of a Muslim, there are certain rights to the property left behind. These rights have been specifically determined by God specifically under faraid law.
- The distribution of fares to those who have legal rights MUST be fulfilled and FARDU KIFAYAH to the Muslims (especially the heirs) to settle them.

What is HIBAH?
In terms of language: – means GIFT.
In terms :- is a voluntary act of giving from one party to another voluntarily without recompense (iwad), hoping for the reward of the end and glorifying one using the words of devotion and qabul.
There are three types of HIBAH: –
- Absolute HIBAH – HIBAH are given directly during alive. Examples: – A house that is already debt-free is leased / provided to children.
- Conditional HIBAH – HIBAH are awarded to the grantor on condition that the grantor dies. Examples: – Conditional grant is a TAKAFUL grant where the grantor receives compensation / grant when the grantor leaves the world.
- Secured HIBAH – Real estate loans still in loan / financing. Examples: – Wasiyyah shoppe is one of the first companies in Malaysia that is believed to assist the grantor in managing a secured grant in accordance with Islamic law.
